Knee Replacement Surgery: The Procedure and Post-Surgical Expectations
Are you or a loved one thinking about getting a knee replacement?
People with severe knee pain are now routinely treated with knee replacement surgery. What exactly is this process, and what can you anticipate happening after it?
Whether you're seeking for information for yourself or a loved one, this guide will arm you with the facts you need to make an informed decision about knee replacement.
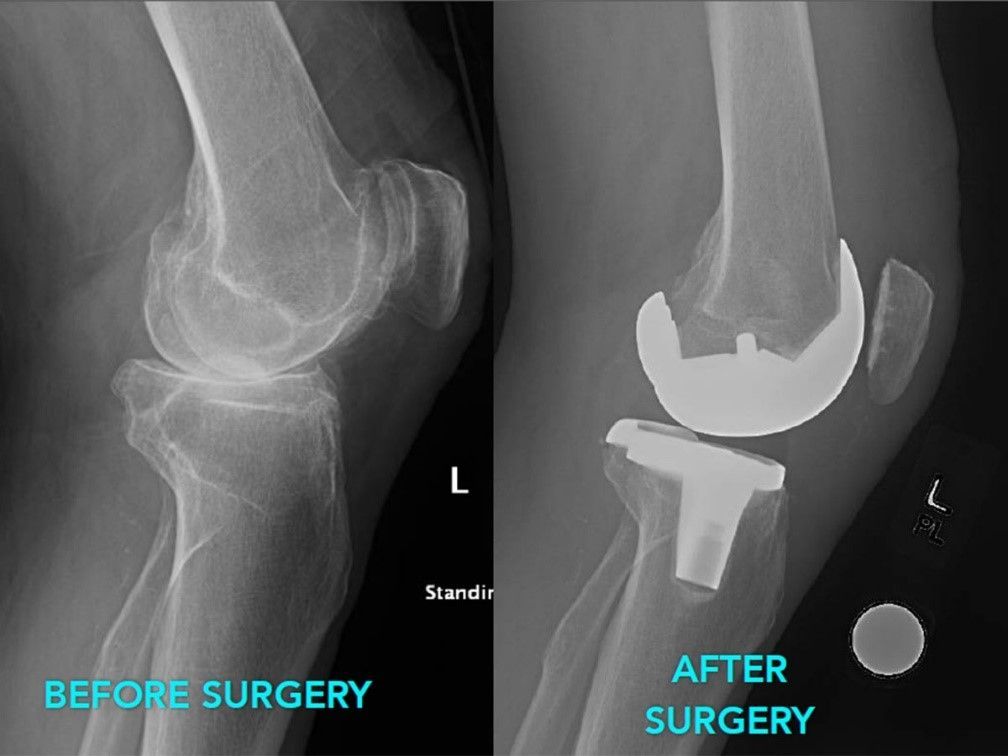
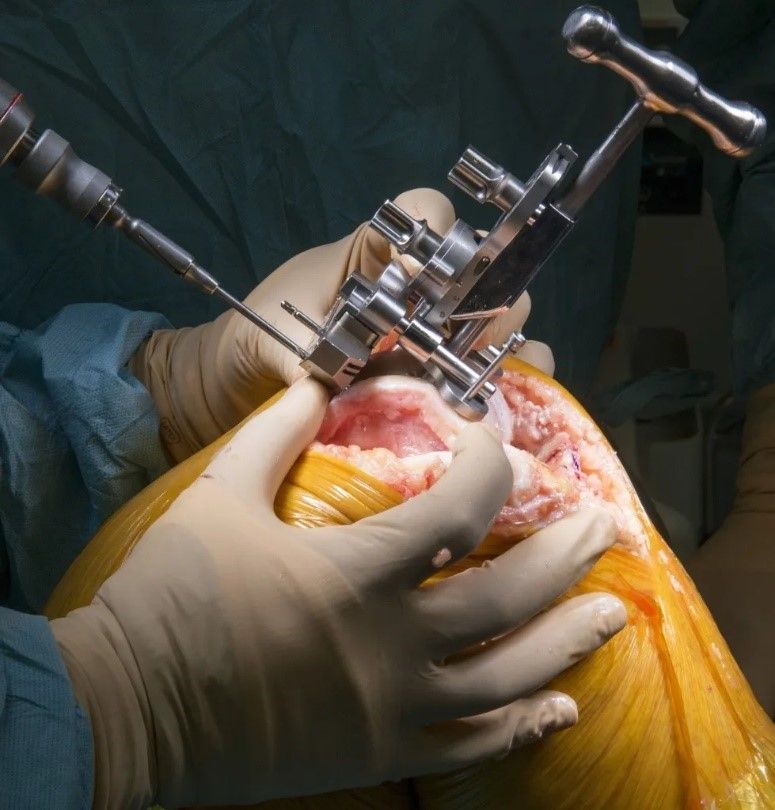
Knee replacement surgery is a surgical procedure that involves removing damaged parts of the knee joint and replacing them with artificial mechanisms. This procedure is performed under general anesthesia and includes the following steps:
- Incision: The surgeon will make an incision in the front of the knee, exposing the knee joint.
- Bone preparation: The damaged femur (femur) and tibia (tibia) ends are carefully cut and shaped to put the artificial components in place.
- Implant placement: Artificial joint, including metal alloys and high-density plastics, are introduced into the prepared bone surface. The components can be cemented in place or pressed, allowing the bone to grow into an implant.
- Patella resurfacing (optional): If the back of the kneecap (patella) is damaged, it may be covered with a plastic component to improve joint function.
- Closure: The incision is closed with sutures or staples, and a sterile dressing is applied.
The whole process takes about two hours, although this time can vary depending on the difficulty of the case. After surgery, you will be taken to a recovery area, where medical staff will carefully monitor your vital signs and ensure your comfort.
Recovery and rehabilitation after knee replacement surgery
A focused rehabilitation and rehabilitation program following knee replacement surgery is essential for a successful outcome. What to expect throughout the recuperation stage is as follows:
- Hospital stay: After having a knee replacement, most patients stay in the hospital for one to three days. You'll be given painkillers, medicines to stop an infection, and physical therapy to speed your recovery during this period.
- Pain management: After surgery, pain and stiffness are common, but your medical team will make every effort to keep you as comfortable as they can. To control pain, doctors may prescribe medicines like opioids and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). Inflammation and discomfort can also be lessened by applying ice and elevating the leg.
- Rehabilitation exercises: In the process of healing, physical therapy is crucial. You will be led through a series of exercises by your physical therapist in order to increase the strength, flexibility, and range of motion of your new knee. Walking, light stretching, and exercises with weights or resistance bands can all be included in these workouts.
- Assistive devices: You might need to walk with crutches, a walker, or a cane in the beginning of your recovery. While your knee recovers and heals, these devices offer stability and support.
- Slow restart: You can gradually get back to your regular activities as your knee recovers and your strength grows. You'll be informed when it's safe to drive, work, and engage in sports by your surgeon and physical therapist.
Physical therapy exercises for knee replacement patients
Physical therapy is an essential part of recovery from knee replacement surgery. Physiotherapists often prescribe the following exercises to help improve strength, flexibility, and range of motion in the new knee joint:
- Quadriceps sets: Sit in a chair with your legs stretched out in front of you. Squeeze the front of the thigh and hold for a few seconds. Relax and repeat a few sets.
- Straight leg raises: Lie on your back with one leg straight and the other bent. Lift your right leg off the ground, keeping your knee straight. Hold the position for a few seconds and lower it. Repeat a few sets on each leg.
- Heel slides: Lie on your back with your legs straight out. Slide your heels toward your buttocks by bending your knees. Slowly return to the starting position. Repeat the operation for several series.
- Hamstring curls: Stand behind a chair with your feet shoulder-width apart. Bend one knee and bring your heel toward your butt. Slowly lower your legs. Repeat a few sets on each leg.
- Step-ups: Stand in front of a step or stairway with your feet shoulder-width apart. Step up the stairs with one foot, then step up with the other. Step back and repeat with the other leg. Repeat the operation for several series.
- Standing knee flexion: Stand facing a wall or cling to a chair for support. Bend your knees and bring your heels toward your buttocks. Hold for a few seconds, then lower your legs. Repeat a few sets on each leg.
It's important to do these exercises as directed by your physical therapist and slowly increase the intensity and duration as your knee strength increases. Consistency and patience are the keys to achieving the best results.
Common reasons for knee replacement surgery
For those whose quality of life is compromised by severe arthritis, knee replacement surgery is advised. The following are the most typical causes for undergoing this procedure:
- Osteoarthritis: The most common reason for knee replacement surgery is this degenerative joint disease. Osteoarthritis develops over time due to damage cartilage that covers both ends of bones tears away, resulting in swelling, discomfort, and stiffness in the knee joint.
- Rheumatoid arthritis: Rheumatoid arthritis, in contrast to osteoarthritis, is an inflammatory condition that results in joint inflammation, notably in the knees. This inflammation has the potential to damage joints over time, necessitating knee replacement surgery.
- Post-traumatic arthritis: An injury to the knee, such as a ligament tear or fracture, might make the damaged joint more susceptible to developing arthritis. Knee replacement surgery may be required if more conservative methods of pain management are unsuccessful.
- Other conditions: Patients with illnesses including avascular necrosis, problems with the blood flow to the bones, or tumors in the knee joint, surgeons may also advise to have knee replacement surgery.
Types of knee replacement implants
There are many types of knee replacement implants available, and the choice of implant will depend on various factors, including the patient's age, activity level, and the condition of the knee joint. The most commonly used knee replacement implants include:
- Total knee replacement (TKR): This is the most common type of knee replacement surgery, which is also known as total knee arthroplasty in which all three compartments of the knee joint (medial, lateral, and patellar) are replaced by an artificial knee.
- Partial knee replacement (PKR): If the damage is limited to one compartment of the knee, a partial knee replacement can be performed. This includes replacing only the affected cavity, keeping healthy portions of the knee joint.
- Revision knee replacement: In some cases, a previously implanted prosthetic knee may need to be replaced due to looseness, wear, or infection. Modified knee replacement surgery involves removing old parts and replacing them with new ones.
- Gender-specific knee implants: Some manufacturers offer specially designed knee replacement implants for male or female patients, due to differences in knee anatomy and mechanics between the sexes.
Your orthopedic surgeon will determine the best type of knee replacement implant for your specific needs. It is essential to discuss the various options with your surgeon and understand the possible advantages and disadvantages associated with each option.
Preparing for knee replacement surgery
To guarantee a smooth procedure and rehabilitation after knee replacement surgery which is also known as knee arthroplasty, proper planning is essential. Here are some crucial actions to take:
- Health Rating: Your knee joint's health and condition will be thoroughly evaluated by your orthopedic specialist. To ascertain your suitability for surgery, a physical examination, imaging studies, and blood tests may be used.
- Drug Evaluations: Inform your surgeon of any supplements you take because some may need to be changed or stopped right before surgery. Blood thinners fall under this category since they raise the possibility of blood clotting during the surgery.
- Alterations in your way of life: It's crucial to stop smoking a few weeks before surgery if you smoke. Smoking can make it harder for your body to repair and amplify the possibility of difficulties. A good diet and regular exercise can also help you feel better and get your body ready for surgery.
- Pre-operative instructions: Your surgeon will provide you with detailed instructions regarding any necessary pre-surgical consultations, antibacterial soap baths, and fasting before surgery. To reduce the possibility of difficulties, it is imperative that you strictly adhere to these recommendations.
- Support system: Bring a friend or family member with you to the hospital the day of the procedure and ask them to assist with your care and transportation while you are recovering. The shift to daily activities can be greatly facilitated by having a support structure in place.
The knee replacement procedure explained
FAQs
-
What do they do in a knee replacement?
Damaged knee joint parts are removed during knee replacement surgery and replaced with prosthetic joints consisting of metal, plastic, or a combination of both materials. Under general anesthesia, the procedure often takes 2 hours.
-
How long does it take to recover from a knee replacement?
Recovery times for knee replacement surgery vary, but most patients can anticipate being able to walk again with support in the days to weeks following surgery. The knee may need several weeks or months to fully recover and regain its strength and mobility. Physical therapy is frequently advised to speed up the healing process.
-
What is the most important thing to do after knee surgery?
It is crucial to adhere to your doctor's aftercare recommendations following knee surgery. Physical rehabilitation, using painkillers as prescribed, and maintaining a dry and clean surgery site may all be part of this. It's also crucial to rest and refrain from overusing the injured knee until the doctor gives the all-clear to get back to your regular routine.
-
How long does it take to walk after knee surgery?
The length of time that you may walk following knee surgery depends on the procedure and the patient. After surgery, the patient can often start using crutches or a walker a few days to a week later. The knee's ability to move freely and with full strength may not return for several weeks or even months.
What do we look for in a surgeon that performs Knee Arthroplasty?
- Our Surgical Sources must be comfortable sending their family members to the surgeon.
- The surgeon must specialize in knee arthroplasty and be a high-volume surgeon.
- The surgeon must be board-certified and have a good track record of successful surgeries.
- The surgeon must be performing knee arthroplasty weekly.
- The surgeon must use the latest technology and equipment.
- The surgeon must have good hand-eye coordination.
Surgeon Researcher - Final Words
The best predictor of successful surgery is the skill level of your surgeon. Surgeons are NOT created equal.
Studies, and our experience, show that patients who are operated on by the most skilled surgeons have lower rates of revision surgery, complications, infection, pain, opioid use, and death. The most skilled surgeons achieve the best surgical outcomes - providing you with the quickest recovery and best quality of life.
Finding the most skilled surgeon can be an impossible task if you do not work in the medical industry. Surgeon Researcher is here to change that.
The only sources that know how skilled a surgeon really is are in the operating room with surgeons on a consistent basis.
We talk to these sources.
We are the only service dedicated to finding patients like you the most qualified surgeons in the country by going straight to the source. Our goal is to equip you with all the information you need to make an informed choice about your health care.
Here at Surgeon Researcher, we prioritize the needs of our customers. We are advocates for the patients, not surgeons.
Don't risk your future quality of life. Get in touch with Surgeon Researcher so we can ensure a qualified surgeon is performing your surgery. You can rely on us to be your advocate in the fight for better surgical outcomes.
Do you want to make sure you are seeing a skilled surgeon?
We're here to assist you in making informed decisions about your surgeons.
We will get back to you as soon as possible
Please try again later

